The key to transformational leadership is based upon satisfying basic needs and meeting higher desires though inspiring followers to provide newer solutions and create a better workplace. Transformational leaders actually employ charismatic behaviors and motivate subordinates to provide better outcomes, more profitability, and satisfying careers. These leaders focus on the critical human assets such as commitment and thus help followers to effectively implement organizational changes with both efficiency and effectiveness. It is this leadership style that sheds light on the strategic role of follower attitudes and values to accomplish a higher degree of effectiveness, and highlights the importance of employees in implementing changes at the organizational level. Today’s global business environments involve a high level of uncertainty, organizations will increasingly need more transformational leaders to be more innovative and creative.
The following characteristics will make for high impact and effective transformational leaders, who represent effective leaders working in today’s knowledge-based economy, can develop and manage intellectual capital in corporations.
- Transformational leaders develop a shared vision and improve relationships with followers; transformational leaders also concentrate on identifying employee’s individual needs and empower followers in order to build a learning climate and mobilize follower support toward the goals and objectives at the senior organisational level.
- Transformational leaders propel knowledge sharing in the company to generate more innovative ideas and solutions for new and demanding issues that come up constantly in our hypercompetitive economic environment.
- Transformational leaders focus on inspiring people and not just treat them as human assets. This sets a higher level of desired expectations for them.
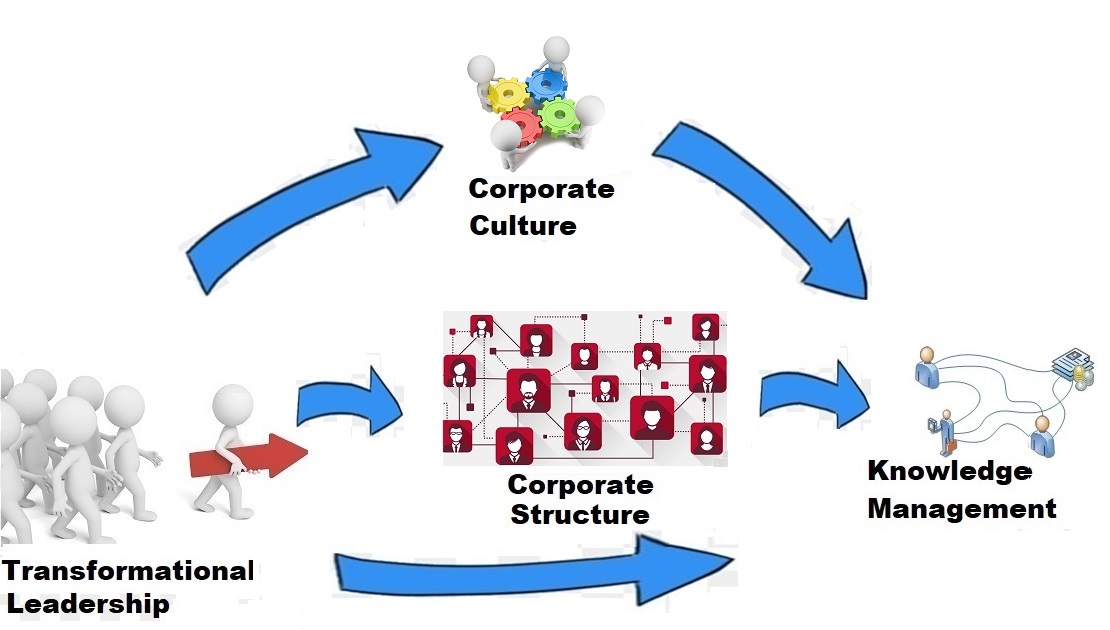
A Transformational Leader’s Toolbox to Build a Strong Culture and Structure
Corporate culture includes three dimensions: collaboration, trust, and learning. Transformational leaders facilitate collaboration to develop relationships in organizations. A transformational leader contributes to the cultural aspect of trust, through considering both employee’s individual interests and company’s essential needs. Also, transformational leaders identify individual needs of their employees and develop a learning culture to generate new knowledge and share it with others. Transformational leaders can, therefore, manipulate a firm’s culture (collaboration, trust and learning) to conform to the needs and expectations of strategic goals and objectives.
Corporate structure can be reshaped by transformational leaders when they develop knowledge sharing and inspire employees to create new ideas for a better environment among business-units and departments. Informal structure could facilitate new idea generation to build a more innovative climate within organizations. Transformational leaders are known to implement organizational changes that develop better collaboration among subordinates and managers. Centralized versus decentralized decision making is a topic that transformational leaders must deal with. Scholars found that more emphasis on formalized and mechanistic structures can negatively impact the transformational leader’s ability to exert such changes. On the contrary, a more decentralized and organic structure may enable transformational leaders to improve departmental and managerial interactions. The mechanical or centralization at the commanding level of transformation leadership impairs the opportunity to develop relationships among managers, business units, and departments. Thus, transformational leaders are top management executives who enhance decentralized and organic structures to develop relationships and interactions within organizations.
The Impact of Change on Knowledge Management Performance
Corporate culture plays a critical role in exploiting organizational knowledge. Collaboration provides a shared understanding about the current issues and problems among employees, which helps to generate new ideas within organizations. Trust towards their leader’s decisions is a necessary precursor to create new knowledge. Moreover, the amount of time spent learning is positively related with the amount of knowledge gained, shared, and implemented. Therefore, transformational leaders can reshape, and in some cases, manipulate corporate culture to create a more effective knowledge cycle within departmental and business units of organizations. #
Corporate structure can be reshaped by transformational leaders to be more effective when the command center of organizations can disseminate information in a decentralized and organic way as opposed to the mechanical and centralized command center. Decentralized structures shift the power of decision-making to the lower levels and subsequently inspire organizational members to create new ideas and even implement them while centralized structures may negatively impact interdepartmental communications and inhibit knowledge exchange. Ergo, transformational leaders positively contribute to organizational knowledge management through building more decentralized and organic structures within organizations. The following figure provides a snapshot of how transformational leadership, corporate culture and corporate structure are linked.
While I acknowledge this work and encourage more of it, I primarily focus on practical applications for executives. Things that can be used immediately and applied to the bottom line to improve profitability and revenue. I stress that knowledge is a strategic resource for organizational portfolios. Many organizations still implement knowledge management initiatives without sufficient consideration of their organizational leadership. When executives ensure the effectiveness of knowledge management projects they increase control and lesson operational risk.
This article raises vital questions as to how executives can successfully contribute to knowledge management and subsequently improve performance at all levels of the organization. Executives can now see how transformational leaders not only can directly support knowledge management, but it can also cultivate an effective corporate culture and add to structural initiatives, which will enable knowledge management processes within organizations.
Executives can also see that cultivating an effective culture coupled with structural issues requires developing transformational leadership within organizations—not only at the higher echelons of the organization but at every level. Thus, in light of the increased pressures of the global workplace that inspires leaders to exert effective change at the organizational level, this article points out the vital importance of transformational leadership in reshaping an organization’s internal resources to have access to more effective structural initiatives and higher performing culture within organizations. I, therefore, suggest that corporate culture and corporate structure constitute the foundation of a supportive workplace to improve knowledge management and reduce operational risk. In fact, I suggest that if corporate culture and structural initiatives are not completely in favor of supporting knowledge management, organizations cannot effectively implement knowledge management projects and may become obsolete, taken over, or acquired. Accordingly, I suggest that executives channeling knowledge management efforts into organizational constructs, engaging in the practice of transformational leadership, and employing a supportive corporate culture and structural platform within organizations.